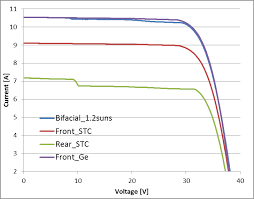
A promising approach to increase the yield of photovoltaic devices are bifacial solar cells and modules. These devices use the same or even a reduced amount of resources but allow higher output power densities due to the double-sided power generation and thus further reduce levelized cost of electricity. An important step is the accurate measurement of the current-voltage (IV) characteristics of the cells under realistic conditions within a setup that is applicable in industry. The most accurate option is to illuminate the cells simultaneously from both sides. Single-sided illumination is easier to realize, but the accuracy of such an approach has not yet been shown. In order to be able to illuminate and measure bifacial solar cells from the front and the rear side simultaneously in one step, the automated cell tester in the PV-TEC laboratory at Fraunhofer ISE was upgraded in cooperation with the companies h.a.l.m. elektronik and JRT Photovoltaics by a bifacial measuring setup with an additional flash box for simultaneous and independent front- and rear-side illumination. Since the rear-side flash box cannot be installed vertically under the solar cell for spatial reasons, a tilted mirror is required which directs the light from the horizontally installed flash box to the rear side of the solar cell. The 45° tilted mirror is mounted on a linear axis and can be moved from the measuring position into a protected rest position under the flash box when it is not in use. In addition to an aluminum-coated mirror which is designed to reflect the light with respect to its spectrum as unchanged as possible to the solar cell, other reflectors can also be installed on the mount of the linear axis, which allows the electrical parameters of the solar cell to be measured in dependence of specific reflectors, e.g. roofing tiles or floor covers, representing different albedos [1,2]. In order to prevent the front and rear illumination affecting each other, the upper part of the measuring chamber is separated from the lower part by a black plate with a cutout, which corre-sponds exactly to the contour of the solar cell to be measured. A second monitor cell is mounted face down beside the solar cell under test. With the described measuring station measurements under real operating conditions and the valida-tion of the linearity of different cell are possible.